In the constantly evolving world that is project management knowing the basic components of Jira is essential for teams looking to improve their efficiency and simplify their workflows. If you’re an experienced project manager or you’re just beginning your journey on Atlassian’s powerful platform, understanding Jira issues is crucial to ensure a successful delivery of your project.
What Are Jira Issue Types and Why Do They Matter?
Jira issue types form the basis of organization for projects in the Jira platform. Based on Atlassian’s own documentation These kinds of work “distinguish different categories of work” and assist team members “search and sort the work your team takes on, track the progress of specific types of work.”
The four main issues which are Epic, Story, Task and Bug form an orderly structure that allows organizations to cut down complicated projects into manageable parts and maintain clear visibility at every level of the work.
The Complete Jira Issue Type Hierarchy
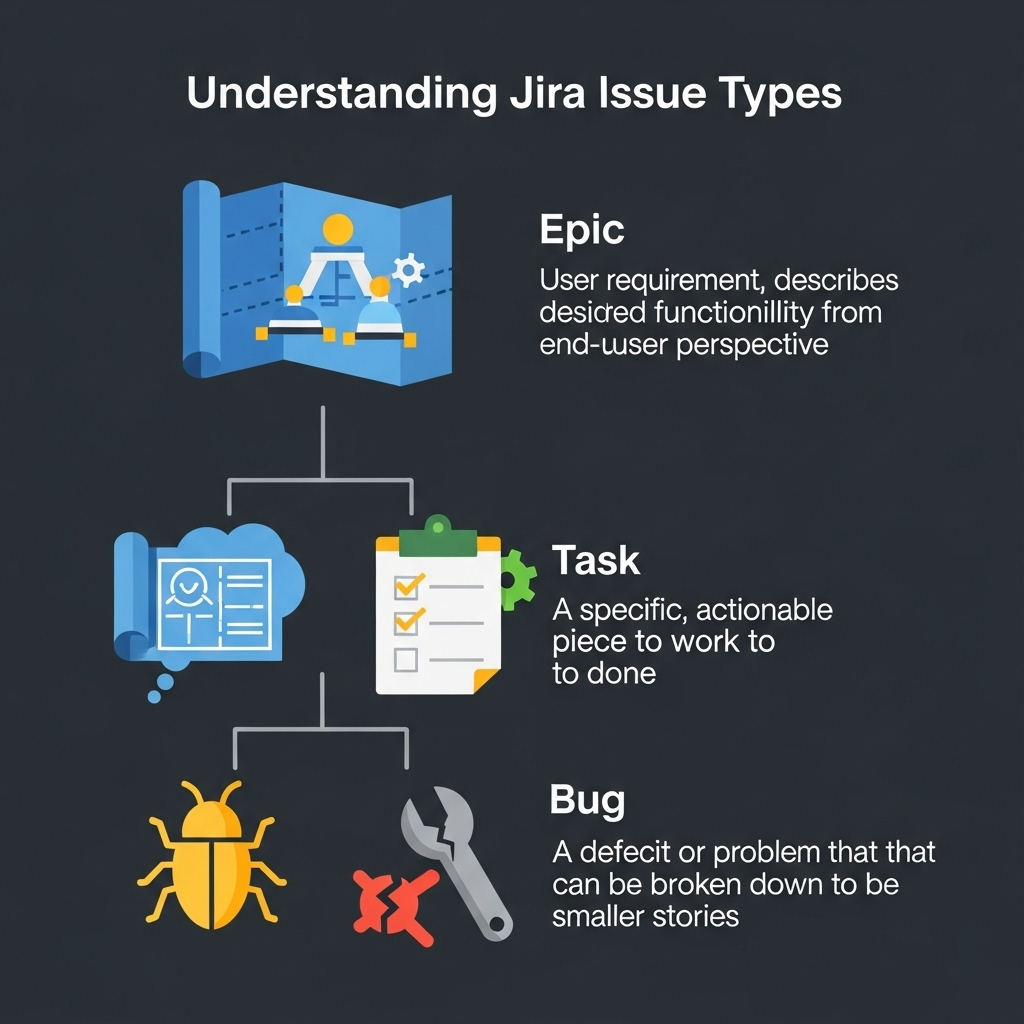
Epic: The Strategic Foundation
Epic is a type of work that Epic represents the highest degree of work within Jira’s hierarchy default. According to BigPicture, “Epic is a large body of work that can be broken down into smaller tasks or stories” and “represents a significant project milestone or a larger feature that will take multiple sprints to complete.”
Key Characteristics of Epics:
- Scope: Large projects that span several sprints or releases
- The typical duration is 2 to 6 months of work on development
- The purpose of this program is to align strategically and high-level tracking of progress
- Example: “Implement new user authentication system,” “Launch mobile application,” “Redesign checkout process”
Best Practices for Epic Management:
- Make sure to keep Epic descriptions focussed on the business benefits and results
- Set out clear success criteria and acceptance standards
- Reduce Epics into 8-15 stories for the best management
- Utilize Epic Burndown Charts to monitor the progress of your burndown over time.
Story: The User-Centric Building Block
User Stories are the smallest piece of work that provides value to the end-users. In accordance with Atlassian’s policies, “A user story is the smallest unit of work that needs to be done.”
Essential Story Components:
- Persona of the user: Who can benefit from this feature?
- Functionality What does the user want to achieve
- Business value The importance of this feature
- Acceptance criteria The definition of done
Story Writing Best Practices:
- Use the following format: “As a [user type], I want [functionality] so that [benefit]”
- Keep stories brief enough to finish within one sprint
- Provide detailed acceptance criteria
- Estimate using story point for an approximate size
Task: The Actionable Work Item
Tasks are specific tasks which must be accomplished however they may not directly connect to the user’s functionality. According to Tech Upscale Tech Tasks allow the ability for groups for teams to “add issues to sprints over two different levels.”
When to Use Tasks:
- Technical debt resolution
- Improvements to infrastructure
- Documentation updates
- Work in research and investigations
- Administrative tasks
Task Management Tips:
- Make sure you are specific and take action in the task descriptions.
- Assign the clear title and due dates
- Linking related tasks to ensure the context
- Labels and components can be used for better organization
Bug: The Quality Assurance Essential
Bugs are problems that affect or hinder software functionality. According to Atlassian’s definition of bug “A bug is a problem which impairs or prevents the functions of a product.”
Bug Classification Levels:
- Critical Systems: System crashes and data loss, as well as security flaws
- The Highest: Significant functionality not working with significant impact on users
- Medium: Minor issues with functionality Workarounds are available
- Cosmetic issues little impact on users
Effective Bug Management:
- Include detailed reproduction steps
- Include screen captures or screenshots
- Provide information about the browser and environment
- Link to similar Stories or Epics where appropriate.
Track Changes in Your Project: Advanced Monitoring Strategies
Modern project management requires real-time transparency into changes in projects and advancement. Harvard Business Review research shows it is “only 35% of projects today are completed successfully,” that highlights the significance of effective tracking changes.
Essential Change Tracking Features:
- Activity Streams: Track all issues in real-time
- Custom Dashboards. Create customized views of the project’s metrics
- Automated Notifications: Be up-to-date on important changes
- Audit Logs: Keep the complete history of changes
- Integration Alerts: Integrate to other tools to provide a comprehensive monitoring
Advanced Tracking Techniques:
- Use JQL (Jira query language) to perform more complex searches
- Make use of Confluence integrations for document monitoring
- Create automated workflows to facilitate changes that require approval
- Create custom fields to meet specific requirements for tracking
Test It For Free Today: Start with Jira
Atlassian provides a variety of options for teams to start with their Jira journey. The free plan can accommodate up to 3 users and comes with important features for smaller teams to get started exploring Jira’s capabilities.
Free Plan Includes:
- The four main issue types (Epic, Story, Task and Bug, Story, Epic)
- Basic workflow management
- Scrum as well as Kanban boards
- Community assistance
- 2GB of storage
Upgrade Path Considerations:
- Standard Plan ($7.75/user/month) Standard Plan: Unlimited storage, advanced search
- Premium plan ($15.25/user/month) Advanced roadmaps, sandbox environments,
- Enterprise plan (Custom pricing) High-end security, unlimited storage and premium support
Pricing and Plans: Making the Right Investment
Understanding the pricing structure of Jira is vital for budgeting and access to features. Based on the current Atlassian pricing teams must take into account both the immediate requirements and growth projections.
Cost-Benefit Analysis:
- ROI Calculation: Think about time savings from automation, as well as better organization
- Scalability: Consider the expansion of teams and the requirements for features
- Integration Costs: Be aware of Marketplace apps and third-party integrations
- Training Investment Plan for the team’s onboarding as well as certification
Hidden Costs to Consider:
- Marketplace App subscriptions
- Additional storage capacity beyond the plan limit
- Premium Support Services
- Customization and integrations as well as custom development
AI-Human Collaborations: The Future of Project Management
The combination of artificial intelligence and the human management of projects is changing the way teams work Jira issues types. As per NC State University research, “by 2030, 80% of project management tasks will be run by AI, powered by big data, machine learning (ML), and natural language processing.”
AI-Enhanced Issue Management:
- AI-powered Issue Creation AI is able to analyze the requirements of clients and recommend issue types that are appropriate
- Automatic Prioritization: The machine Learning algorithms can prioritize tasks and bugs according to the impact
- AI can predict future events. AI is able to predict project deadlines and the need for resources.
- Smart Assignments- Automated assignments depending on the team member’s skills and work load
Current AI Implementations:
- Atlassian Intelligence: AI built-in capabilities to Jira Cloud Premium and Enterprise
- The Smart Suggestions feature AI powered recommendation for categorization and linking of issues
- Automated Workflows rules-based automation of issues that require changes
- Predictive Insights based on data: Forecasting based on data to plan projects
Future AI Capabilities:
- Virtual assistants for project management to provide real-time assistance
- Advanced risk detection and mitigation
- Quality assurance and automated testing
- Intelligent resource optimization
JSM is Now the New JSD: Service Management Evolution
Jira Service Management (JSM) has seen significant improvements over it’s predecessor Jira Service Desk (JSD). As per recent Atlassian upgrades, JSM now offers upgraded capabilities to support IT service management as well as customer support.
Key JSM Enhancements:
- Advanced Incident Management Better capability for alerting and response
- Asset Management: Complete tracking of IT resources and dependencies
- AI-Powered Customer Support: Artificial Service Agents and intelligent routing
- Enhanced Reporting: Advanced Analytics and performance metrics
JSM Issue Types:
- Incident: Service disruptions requiring immediate attention
- Issue: Root cause analysis to identify recurring issues
- Change: Modifications planned to IT infrastructure
- Service Request: User-standard request for IT services
Migration Considerations:
- Existing JSD instances are automatically changed to JSM
- New pricing structure based on consumption charging for advanced features
- Improved integration capabilities for tools for development
- Better mobile experience for Field service teams
Best Practices for Issue Type Implementation
Organizational Strategy
1. Create clear Definitions Develop a comprehensive document that defines the appropriate time to use each type of issue. This helps avoid confusion and assures the same usage across teams.
2. Implement Naming Conventions
Standardize names for various issues:
- Epics: “EPIC: [Business Objective]”
- Stories: “USER: [User Action]”
- Tasks: “TASK: [Specific Work]”
- Bugs: “BUG: [Problem Description]”
3. Configure Custom Fields
Create custom fields relevant to every type of issue:
- Epics business value, strategic alignment and success metrics
- Stories The Story Points: Story points, acceptance criteria User personas, acceptance criteria
- Tasks: Estimating Effort Skills, requirements for skill, dependencies
- Bugs: Severity, Environment and reproduction steps
Workflow Optimization
1. Design Appropriate Workflows
Create customized workflows for every problem type, that are reflective of your team’s workflow:
- Epic Workflow: Ideation – Planning – In Progress – Review – Done
- Story Workflow: Backlog – Ready – In Progress – Review – Done
- Task Workflow: To Do – In Progress – Review – Done
- Bug Workflow: Open – In Progress – Testing – Resolved – Closed
2. Implement Automation Rules
Automated systems can be set up to minimize the manual labor:
- Auto-assigning issues based on parts or labels
- Problems with transition parents after all children are completed
- Notify users of bugs with high priority
- Epic update progress dependent on Story conclusion
Team Collaboration
1. Regular Grooming Sessions
Conduct regular backlog refinement meetings to:
- Divide Epics into appropriate-sized stories
- Task effort
- Prioritize bugs based upon their severity and impact
- Review and revise acceptance criteria
2. Cross-Functional Communication
Assist team members in understanding:
- When should you create each type of issue
- How do you write concise descriptions?
- Hierarchy and proper linking
- Responsibility for updating status
Advanced Configuration and Customization
Custom Issue Types
Although the four common issue types can be used to cover the majority of scenarios Teams might require different types to meet specific workflows:
Examples of Custom Issue Types:
- Spike research or investigation work that has uncertain results
- Sub-bug: In depth breakdown of complicated bugs
- Improvement Requests for enhancements that don’t involve new features
- Documentation: Specific tasks for making or modifying documentation
Issue Type Schemes
Configure issue type schemes in order to decide which types of issue are offered in various projects:
- Software Development Projects: Epic, Story, Task, Bug, Spike
- IT Service Projects: Incident, Problem, Change, Service Request
- Marketing Projects: Campaign, Task, Review, Approval
Screen Configurations
Create custom screens for each type of issue so that they display the relevant fields:
- Epic Screens Strategic alignment with business value and time line
- Story Screens Story Screens: Acceptance criteria, story points User personas, story points
- Task Screens: Estimation of Effort and skill requirements Checklist
- The severity of the bug screen and Environment and reproduction steps Attachments
Integration and Ecosystem
Development Tool Integration
Connect Jira with tools for development in order to build seamless workflows
- Bitbucket/GitHub: Link commits and pull requests to issues
- Builds with Jenkins/Bamboo, and deployments following issues that have changes
- Confluence: Link documents with Epics and Stories
- Slack/Microsoft Teams Get notifications and create issues using chat
Reporting and Analytics
Utilize Jira’s reporting capabilities get insight:
- Epic Burndown: Keep track of Epic Progress over Time
- Velocity Charts: Track the team’s capacity to deliver
- Bug Reports: Examine the trends in defect resolution and patterns of defects.
- Custom Dashboards: Design roles-specific views of project information
Third-Party Apps
Increase Jira functionality using apps from the marketplace:
- Advanced Roadmaps: Improved Epic as well as Story Planning
- Tempo: tracking time and resource management
- Zephyr: Management of test case and execution
- Portfolio Planning and tracking of multiple projects
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Monitor relevant metrics for each kind of issue:
Epic Metrics:
- The rate of completion is staggering.
- Time to deliver business value
- Scope creep percent
- Stakeholder satisfaction scores
Story Metrics:
- Rate of story completion per sprint
- Average time for a story cycle
- The accuracy of the story point
- Defect rate per story
Task Metrics:
- Rate of completion of tasks
- Average task duration
- Time to resolve task dependency
- Resource utilization efficiency
Bug Metrics:
- Bug discovery rate
- Mean time until resolution (MTTR)
- Distribution of bug severity
- Customer-reported bugs vs. internal bugs
Continuous Improvement Process
1. Regular Retrospectives
Retrospectives of the team to determine:
- Use of the issue type
- Bottlenecks in the flow of work
- Communication gaps
- Improvements to the configuration of tools
2. Data-Driven Decisions
Make use of Jira report and analysis for:
- Recognize patterns and trends
- Maximize the team’s capacity by plan
- Improve estimation accuracy
- Improve quality of processes
3. Process Refinement
Review and update regularly:
- Issue type definitions, usage and guidelines
- Automation rules and workflow configurations
- Custom field requirements for screen layouts
- Integration configurations, data flows, and data flow
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Issue Type Misuse
Problem: Teams frequently misuse issues types, causing confusion and decreasing effectiveness.
Solutions:
- Give clear instruction on how to use each type of issue
- Make decision trees or flowcharts to help you select the issue type
- Use validation rules to avoid common errors
- Regular audits are conducted to find and correct the misuse patterns
Over-Customization
Problem: Overly customized features can create Jira complicated and hard to manage.
Solutions:
- Start with the standard configurations and gradually customize
- Document all modifications made and the business reasons for them
- Regularly scheduled reviews to eliminate unused field types and custom workflows
- Think about the implications for the future of upgrades, migrations and other changes.
Poor Hierarchy Management
Problem Linking and hierarchy relationships can reduce the visibility of reports and reduce their accuracy.
Solutions:
- Set clear guidelines for Epic-Story-Task relationships
- Automate to ensure correct linking
- Regular cleaning of abandoned and/or incorrectly linked issues
- Training in proper hierarchy management methods
Future Trends and Considerations
Emerging Technologies
1. Advanced AI Integration
- Predictive issue creation based upon user behavior
- Smart test cases generation using user accounts
- Automation of code reviewing and bugs detection
- Intelligent resource allocation and capacity planning
2. Enhanced Collaboration Features
- In real-time, collaborative editing of the description of an issue
- Video integration to improve communication
- Advanced alerting and notification systems for advanced notification and alerting
- Field teams that are mobile-first designed for
3. Improved Analytics and Insights
- Machine learning-powered project forecasting powered by machine learning
- Innovative risk assessments and reduction
- Quality metrics that predict the future and defects prevention
- Dashboards and alerts that are real-time, including performance.
Industry Evolution
1. Agile and DevOps Integration
- Tighter integration between development and operations
- An enhanced pipeline integration for CI/CD
- Automated testing and quality control
- Improvements in delivery and control of releases
2. Remote Work Optimization
- Advanced collaboration tools for teams with distributed locations
- Mobile experience has been improved and offline capabilities
- Advanced video screen sharing and conferencing
- A better time zone, and more cultural concerns
Final Thoughts: Mastering Jira Issue Types for Project Success
Implementing and understanding Jira issues types – Epic Stories, Story, Task and Bug is essential to effective project management in today’s chaotic development environment. In this thorough guide, each type of issue has a particular purpose in the hierarchy of projects and can contribute to overall team efficiency and success of the project.
The shift between traditional collaboration and AI enhancement is an enormous chance for teams to increase their effectiveness and efficiency in delivering. Through the use of Jira’s issue type system together with new AI technology and the best practices, teams will be able to achieve unparalleled levels of transparency control, efficiency, and effectiveness.
If you’re only beginning with Jira’s free plans or are considering an enterprise-wide deployment The most important factor to success is knowing the specific requirements of your team and implementing the right configurations and continually improving your processes on the basis of data-driven insight.
In the years to come, as JSM continues to grow from its JSD beginnings and AI-human collaborative is becoming more commonplace Teams that understand these basic concepts will be the best placed to benefit from future technological advancements and retain their advantage in an ever-changing world of project management.
Key Takeaways:
- Learn to master the four main types of issues and their appropriate application cases
- Establish a an appropriate hierarchy and linking strategy
- Utilize AI and automation features to boost productivity
- Always review and optimize your procedures. Continuously measure and improve your
- Be aware of the latest trends and new technologies.
Following the guidelines and best practices described in this document Your team will be fully equipped to take advantage of the potential of Jira issue types and lead positive outcomes for your projects in 2025 and beyond.